AI and Smart Farming: A Match Made in Agriculture 2025
Individually, both AI and smart farming hold immense promise. Smart farming, with its interconnected sensors, real-time data, and automated systems, brings unprecedented efficiency and control to agricultural operations. AI, with its ability to learn, reason, and make predictions from vast datasets, offers intelligent insights and decision-making capabilities that surpass human capacity. When combined, however, AI and smart farming create a synergistic powerhouse, a match truly made in agricultural heaven, poised to redefine productivity, sustainability, and profitability in the sector.
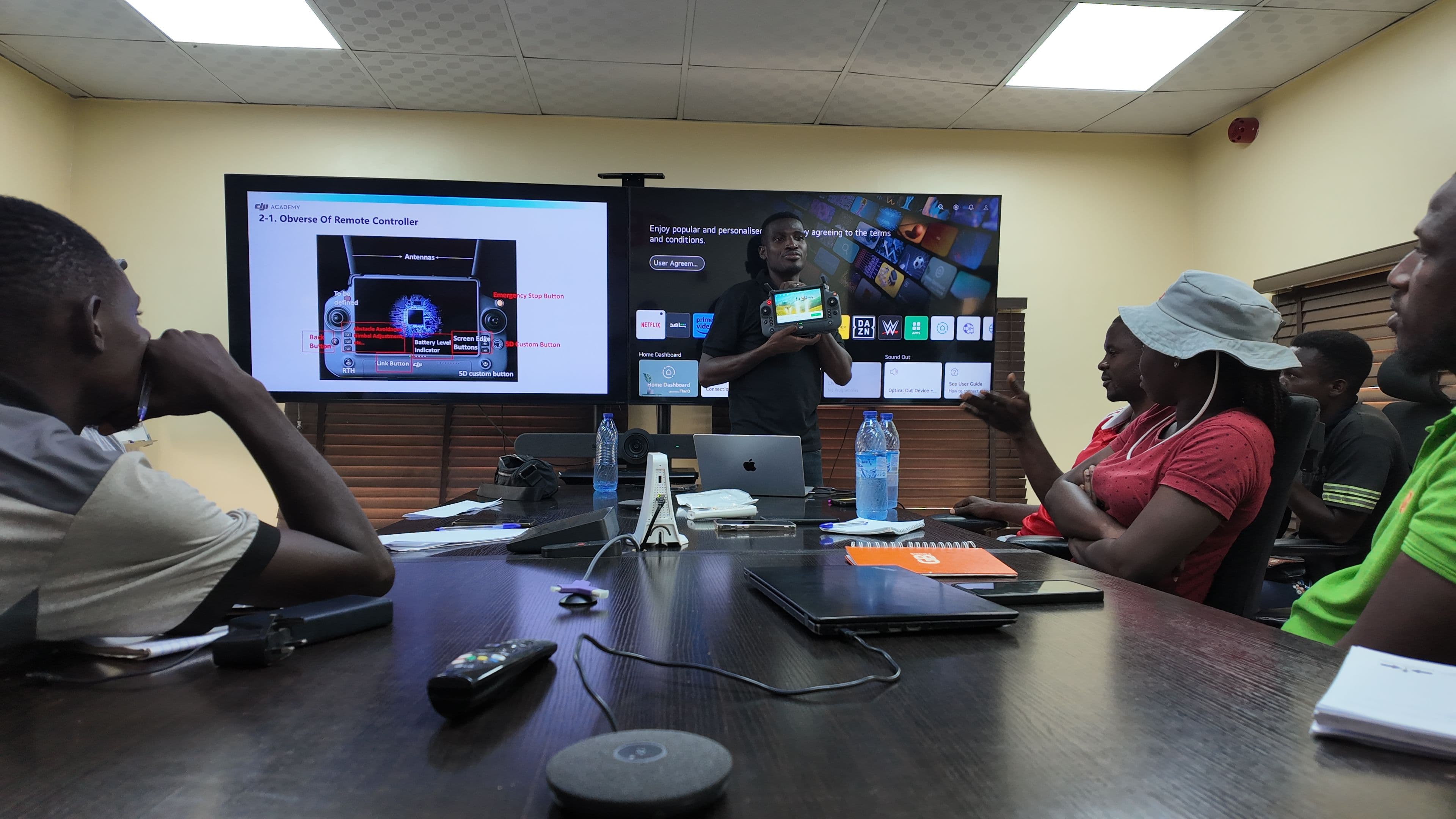

The Foundation: Understanding Smart Farming
Before we dive into the AI revolution, it's crucial to solidify our understanding of smart farming. As discussed previously, smart farming is a holistic approach to agriculture that leverages advanced technologies to create an interconnected and highly automated system across the entire farm. It moves beyond the localised optimisation of precision farming to encompass a broader vision of seamless integration.
Key components of Smart Farming include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): A network of sensors (soil moisture, temperature, nutrient, weather, humidity, etc.), devices (smart irrigation valves, automated feeders), and machinery (tractors, drones) that collect and exchange data in real-time.
- Big Data: The massive volume of diverse data generated by IoT devices, drones, satellites, and farm machinery, including historical weather patterns, soil conditions, crop health metrics, yield data, and equipment performance.
- Connectivity: Reliable high-speed internet connectivity (5G, satellite, Wi-Fi) to ensure seamless data flow between devices, the cloud, and central management systems.
- Automation: Systems that perform tasks with minimal human intervention, such as automated steering, variable rate application, and robotic operations.
- Cloud Computing: Platforms for storing, processing, and accessing vast agricultural datasets and running complex analytical models.
Smart farming's primary goal is to optimise every aspect of the farm for increased efficiency, productivity, and sustainability by providing real-time insights and enabling automated responses. However, to truly unlock the potential of the enormous datasets generated by smart farming systems and to move beyond mere data collection to intelligent action, AI becomes indispensable.
The Catalyst: How AI Elevates Smart Farming
Artificial Intelligence is the brain that powers smart farming's brawn. It's the engine that processes the torrent of data, identifies patterns, makes predictions, and enables intelligent automation. Without AI, smart farming would largely remain a sophisticated data collection and monitoring system. With AI, it transforms into a predictive, proactive, and autonomously optimising agricultural ecosystem.
Here's how AI acts as a catalyst in various aspects of smart farming:
1. Predictive Analytics and Decision Support
AI's ability to analyse historical data alongside real-time inputs allows for highly accurate predictions, moving farming from reactive to proactive.
- Yield Prediction: AI models can analyse soil data, weather patterns, crop health metrics (from satellite imagery, drone data), and historical yield data to predict crop yields with remarkable accuracy. This helps farmers make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, storage, and market strategy.
- Disease and Pest Detection & Prediction: AI algorithms can analyse images from drones or ground-based cameras to detect early signs of plant diseases or pest infestations, often before they are visible to the human eye. Machine learning models can also predict outbreaks based on environmental conditions, historical data, and crop vulnerability, enabling timely intervention and localised treatment.
- Weather Forecasting & Climate Adaptation: While traditional weather forecasts exist, AI can integrate hyper-local sensor data with broader meteorological models to provide highly specific, real-time weather predictions for a farm. This aids in crucial decisions like irrigation scheduling, planting/harvesting windows, and protection against extreme weather events.
- Market Price Prediction: AI can analyse market trends, supply and demand, geopolitical factors, and weather impacts to predict future crop prices, helping farmers decide when to sell their produce for maximum profit.
2. Precision Resource Management
AI refines the concept of precision beyond just mapping, enabling dynamic and intelligent resource allocation.
- Intelligent Irrigation Systems: AI-powered systems analyse soil moisture levels (from IoT sensors), evapotranspiration rates, crop growth stages, and hyper-local weather forecasts to determine the exact amount of water needed and precisely when and where to apply it. This minimises water waste, a critical concern in arid regions, and prevents over/underwatering.
- Optimised Fertilisation: AI models process soil nutrient maps, plant nutrient uptake data (from spectral analysis), and yield goals to recommend precise fertiliser application rates. This "variable rate" approach ensures nutrients are applied only where necessary, reducing runoff, environmental pollution, and input costs.
- Smart Pesticide/Herbicide Application: Using computer vision and AI, smart sprayers can differentiate between crops and weeds or identify specific pest infestations. This allows for targeted, spot application of pesticides and herbicides, drastically reducing chemical usage and its environmental impact, while also protecting beneficial insects.
3. Robotic Automation and Autonomous Operations
AI is the brain behind agricultural robots, enabling them to perceive, navigate, and perform complex tasks autonomously.
- Autonomous Tractors and Machinery: AI powers self-driving tractors that can navigate fields with centimetre-level accuracy using GPS, lidar, and cameras. They can perform tasks like ploughing, seeding, and spraying without human oversight, reducing Labour costs and fatigue.
- Robotic Harvesting: AI-driven robots are being developed to identify ripe fruits and vegetables and harvest them gently. This addresses Labour shortages for manual harvesting and can lead to less produce damage and higher quality.
- Weeding Robots: Small, autonomous robots equipped with AI and computer vision can identify and remove weeds mechanically or by precise micro-spraying, minimising the use of broad-spectrum herbicides.
- Livestock Monitoring and Management: AI-powered cameras and wearable sensors on livestock can monitor individual animal health, detect early signs of illness, track movement patterns, and optimise feeding schedules. Facial recognition for livestock can even help identify individual animals.
4. Crop and Soil Health Monitoring
AI transforms raw sensor data and imagery into actionable insights about the health of the farm.
- Phenotyping and Plant Health Assessment: AI can analyse vast datasets of plant images (captured by drones or ground robots) to assess plant health, identify nutrient deficiencies, detect stress from drought or heat, and even measure plant growth and development (phenotyping) at scale.
- Soil Analysis and Mapping: AI algorithms can interpret data from various soil sensors to create highly detailed, real-time maps of soil composition, moisture content, pH, and nutrient levels, informing planting and fertilization strategies.
- Disease Identification in Livestock: AI can analyse changes in animal behaviour, body temperature, or even vocalisations to detect illness in livestock, allowing for early intervention and preventing the spread of disease.
5. Supply Chain Optimisation and Traceability
Beyond the farm gate, AI contributes to a more efficient and transparent agricultural supply chain.
- Demand Forecasting: AI models can predict consumer demand for specific produce, helping farmers align production with market needs and reduce post-harvest waste.
- Logistics optimisation: AI can optimise transportation routes and storage conditions for harvested crops, minimising spoilage and ensuring fresh produce reaches consumers efficiently.
- Blockchain Integration: While blockchain handles traceability, AI can analyse blockchain data to identify inefficiencies or potential contamination points in the supply chain.
The Symbiotic Relationship: Why They Are Made for Each Other
The partnership between AI and smart farming is inherently symbiotic:
- Smart Farming Provides the Data: AI is data-hungry. Smart farming systems, with their pervasive sensors and interconnected devices, generate vast, continuous streams of real-time data that AI needs to learn, train its models, and make intelligent decisions. Without this data, AI in agriculture would be largely theoretical.
- AI Provides the Intelligence: Smart farming collects the data, but AI makes sense of it. It transforms raw numbers into actionable insights, automates complex decision-making processes, and enables the predictive capabilities that elevate farming beyond mere observation. Without AI, smart farming data could overwhelm farmers without providing clear pathways for optimisation.
This dynamic creates a virtuous cycle: as smart farming systems collect more data, AI models become more refined and accurate. As AI models become more intelligent, they enable more sophisticated automation and optimisation within smart farming, leading to even greater efficiency and more valuable data generation.
Benefits of the AI-Smart Farming Synergy
The combination of AI and smart farming offers a multitude of benefits for the agricultural sector:
- Increased Productivity and Yields: By optimising every input and process, from seed to harvest, AI-powered smart farming can significantly boost crop yields and livestock productivity.
- Enhanced Resource Efficiency: Drastically reduces the wasteful use of water, fertilisers, pesticides, and energy, leading to significant cost savings and environmental conservation.
- Improved Sustainability: Minimises environmental footprint through reduced chemical usage, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and sustainable resource management.
- Reduced Labour Dependency: Automation and AI-driven decision-making address the growing challenge of Labour shortages in agriculture, freeing human workers for more strategic tasks.
- Better Decision-Making: Provides farmers with real-time, data-driven insights and predictive capabilities, enabling more informed and proactive management.
- Higher Crop Quality and Consistency: Optimised growing conditions and precise interventions lead to better quality produce and more consistent yields.
- Enhanced Animal Welfare: Continuous monitoring of livestock health and behaviour enables early detection of issues, improving animal well-being.
- Greater Resiliency: AI-driven predictions for weather and disease help farms become more resilient to environmental and biological threats.
- Increased Profitability: All the above benefits contribute to lower operational costs, higher yields, and better market timing, ultimately leading to increased profitability for farmers.
- Food Security: By optimising food production and reducing waste, this synergy contributes significantly to global food security.
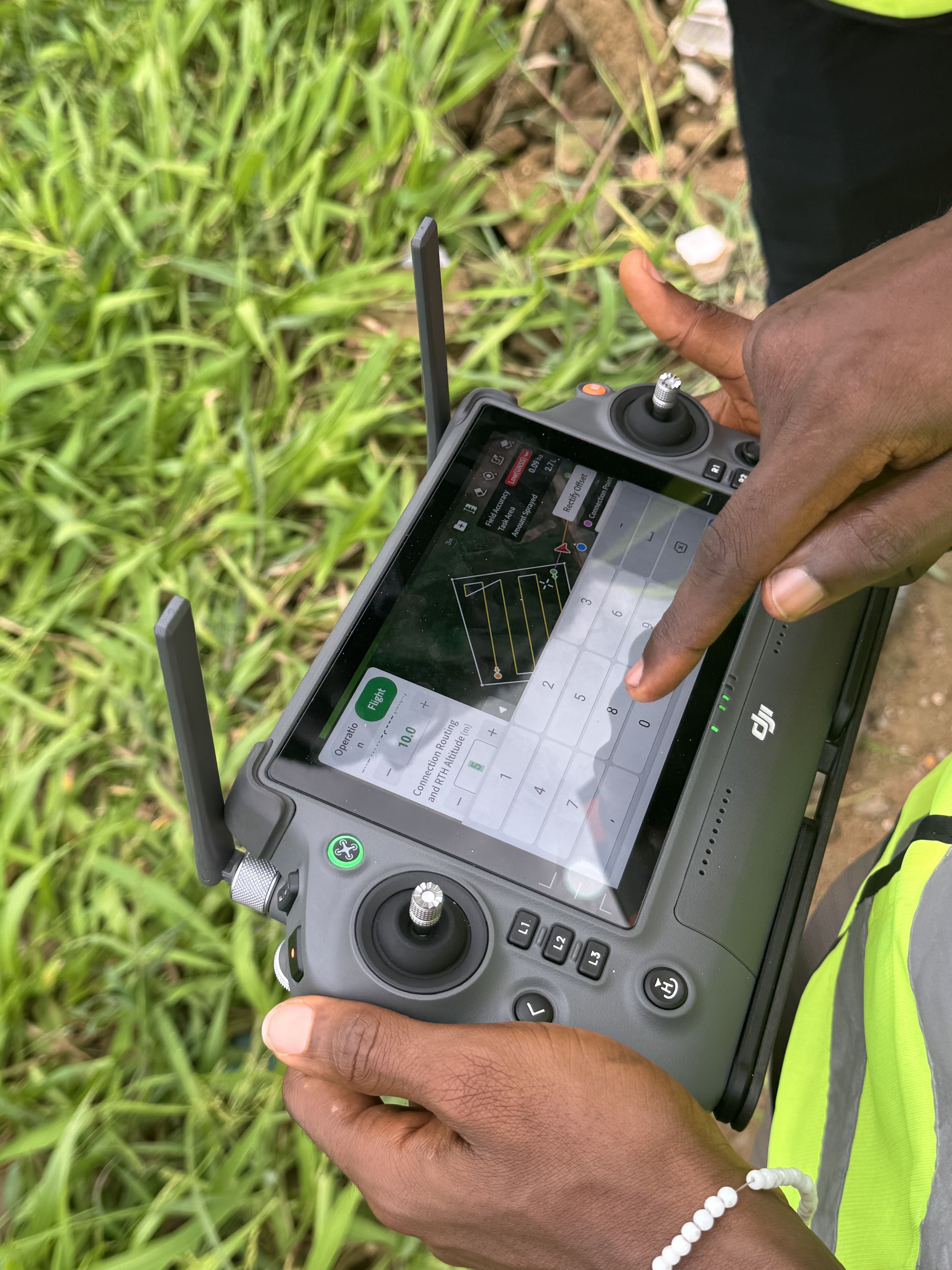

Conclusion
The convergence of AI and smart farming is not merely an incremental improvement; it represents a paradigm shift in how we approach agriculture. It moves us beyond traditional practices into an era of intelligent, data-driven, and highly automated food production. AI provides the intelligence, predictive power, and automation capabilities that transform smart farming's vast data streams into actionable insights and autonomous operations.
This powerful synergy is indeed a match made in agricultural heaven, offering transformative solutions to the most pressing challenges facing our food systems. The era of smart farming and AI in agriculture is not just arriving; with Integrated Aerial Precision, it is already here, ushering in a new paradigm of productivity and ecological responsibility.
Now, take a step ahead and contact us to experience smart farming techniques.


